NASA’s New Space Telescope Will Reveal Secrets of the Universe’s Beginning
NASA’s latest space telescope, the Spherex observatory, successfully launched into orbit on Tuesday, marking a monumental step in the quest to explore the origins of the universe.
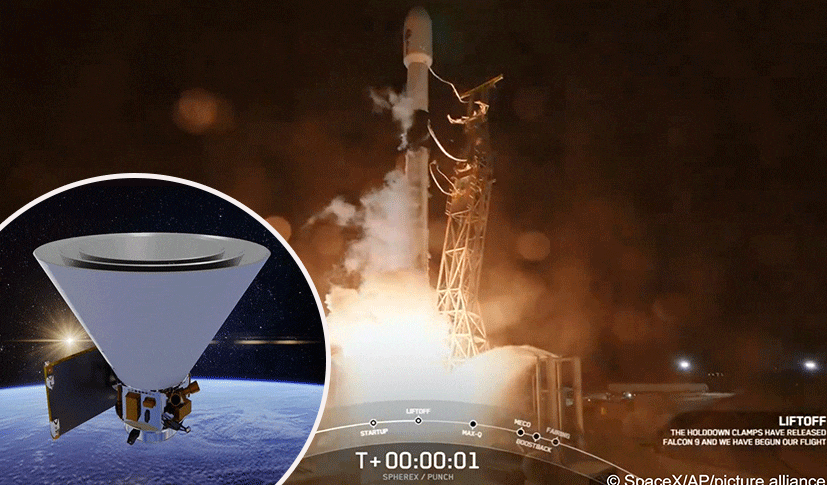
Vandenberg Space Force Base: NASA’s latest space telescope, the Spherex observatory, successfully launched into orbit on Tuesday, marking a monumental step in the quest to explore the origins of the universe. The $488 million mission is set to map the entire sky like never before, offering an unprecedented look at hundreds of millions of galaxies and their cosmic glow since the dawn of time.
Table of Contents
Spherex Mission: A Groundbreaking Space Telescope
Launched aboard a SpaceX rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base, the Spherex observatory is now en route to observe the cosmos from its unique polar orbit. The mission’s primary goal is to provide insight into how galaxies formed and evolved over billions of years and to understand how the universe expanded rapidly in its early moments. The observatory is also tasked with searching for water and other life-essential ingredients in the cold, icy clouds of the Milky Way where new solar systems are being born.
Weighing in at just 1,110 pounds (500 kilograms) — roughly the size of a grand piano — Spherex will spend the next six months mapping the sky with its infrared eyes. The telescope’s wide field of view will allow it to observe not just individual galaxies but the collective glow of galaxies, capturing light from some of the earliest galaxies formed after the Big Bang.
Spherex’s Mission: Unlocking the Mysteries of the Universe
Spherex’s innovative approach differs from other space telescopes like NASA’s Hubble or Webb, which have narrow fields of view and focus on individual galaxies. Instead, Spherex will examine the total cosmic glow produced by all the galaxies combined. This method, known as cosmological glow, will give scientists a fresh perspective on light sources previously missed, offering crucial insights into the origins of galaxies and the universe itself.
According to Jamie Bock, the mission’s chief scientist at the California Institute of Technology, “This cosmological glow captures all light emitted over cosmic history.” By studying this collective light, scientists hope to understand the evolution of galaxies and the aftermath of the Big Bang, revealing secrets about the early universe.
A Colorful Map of the Cosmos
Equipped with advanced infrared detectors, Spherex will be able to capture 102 colors invisible to the human eye, producing the most colorful and inclusive map of the universe ever created. Beth Fabinsky, Deputy Project Manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, described the experience as “looking at the universe through a set of rainbow-colored glasses.”
The telescope is designed to operate in extreme cold, with infrared detectors maintained at minus 350 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 210 degrees Celsius). To achieve this, Spherex features three aluminum-honeycomb cones, which provide insulation from the sun and Earth’s heat, giving the telescope a unique and protective look.
Supporting NASA’s Sun Observation with Punch Satellites
In addition to the Spherex mission, the SpaceX Falcon rocket also carried four Punch satellites to space. These satellites will observe the sun’s corona — its outer atmosphere — and track the resulting solar wind. The combined efforts of Spherex and Punch represent significant advancements in space exploration, promising to expand our understanding of both the far reaches of the cosmos and our closest star.
Also Read: India’s real estate developers opened investment opportunity worth Rs 62,000 cr: Report
Despite a two-week delay due to issues with the rocket, the launch marked a successful step forward in unraveling the mysteries of the universe, providing new tools to study both the depths of space and our solar system.
A New Era of Space Exploration
The Spherex mission represents a major leap in cosmological research, offering insights into how the universe expanded and how galaxies evolved. As the telescope begins its journey to map the sky, it promises to unveil new knowledge about the very building blocks of the universe, offering a unique opportunity to explore the cosmos in ways never before possible.
