Hyderabad: The World Health Organization (WHO) has sounded the alarm once again, declaring a global health emergency due to the rapid spread of the Mpox virus previously known as Monkeypox. As the World Faces Another Health Crisis, Could Another Lockdown Be on the Horizon?
This new threat, reminiscent of the COVID-19 pandemic, has raised concerns about the possibility of another worldwide lockdown. But what exactly is Mpox, and how can we protect ourselves?
What is Mpox?
Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, is a viral illness caused by the Mpox virus, part of the Orthopoxvirus genus in the Poxviridae family. The disease was first identified in monkeys in 1958, giving it its former name. Though it has been known to science for decades, the recent outbreak has caused alarm due to its rapid global spread.
Zoonotic Diseases: The Human-Animal Connection
Mpox is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can be transmitted between humans and animals. Zoonotic diseases, caused by viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi, are known to be severe and life-threatening in some cases, such as rabies. Others, like Mpox, can vary in severity, with symptoms that may improve on their own or require medical intervention.
Understanding the Virus: Two Genetic Clades
The Mpox virus has two genetic clades: clade I and clade II. The current outbreak has been linked to clade IIb, which is responsible for the recent global spread.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
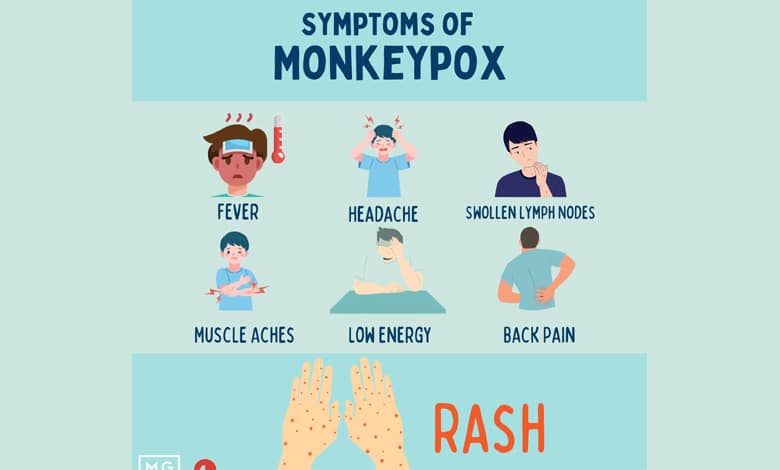
Symptoms of Mpox include a skin rash or mucosal lesions, fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, and swollen lymph nodes. The rash, which can last between 2 to 4 weeks, is often painful and can cause significant discomfort.
How is Mpox Transmitted?
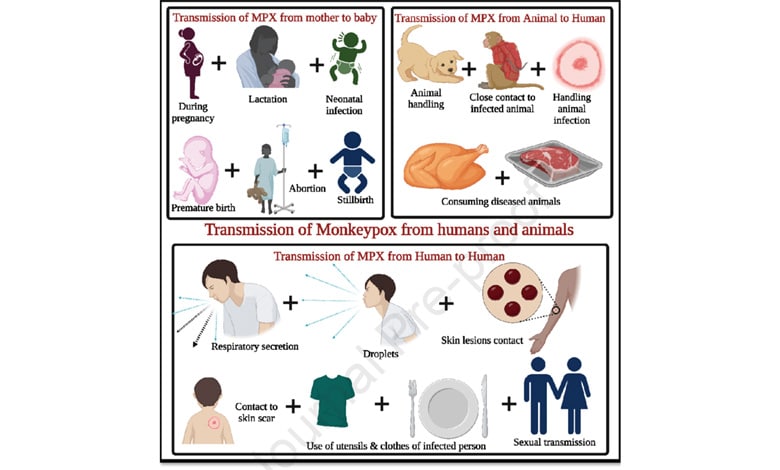
The virus spreads through direct contact with infectious skin or lesions, including face-to-face, skin-to-skin, mouth-to-mouth, and mouth-to-skin contact. It can also be transmitted through respiratory droplets or contaminated materials like sheets or clothing, making close contact a key factor in its spread.
Treatment and Prevention: What You Need to Know
Currently, there is no specific treatment for Mpox, but supportive care is available. Vaccines and therapeutics developed for smallpox may offer some protection. Prevention is crucial and includes avoiding contact with infected individuals and vaccination for those at higher risk.
Global Impact and Response
The outbreak has already resulted in over 14,000 cases and 500 deaths worldwide. WHO, along with various governments, is actively working on a response plan, requiring an initial $15 million in funding to combat the spread of the virus.
Public Health Measures: A Collective Responsibility
Public health measures focus on educating the public about the disease and how to prevent it. Infected individuals are advised to isolate, cover lesions, and wear masks around others to minimize the risk of transmission.
Ongoing Research: A Race Against Time
Scientists are racing to understand the natural reservoir of the virus, improve diagnostic tests, and develop more effective treatments. The global community is on high alert as the world braces for what could be another significant public health challenge.
As the situation unfolds, it is crucial to stay informed and take the necessary precautions to protect ourselves and our communities from the Mpox virus.
